Introduction
Rolling bearings support and guide, with minimal friction (fig. 1), rotating or oscillating machine elements – such as shafts, axles or wheels – and transfer loads between machine components. Rolling bearings provide high precision and low friction and therefore enable high rotational speeds while reducing noise, heat, energy consumption and wear. They are cost- effective and exchangeable machine elements that typically follow national or international dimension standards.
Ball and Roller Bearings
The two basic types of rolling element distinguish the two basic types of rolling bearing :
1 – Ball → ball bearing
2 – Roller → roller bearing
Balls and rollers are different in how they make contact with the raceways.
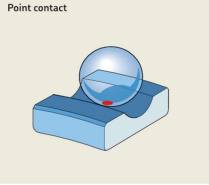
Point Contact : Balls make point contact with the ring raceways (As shown in fig.). With increasing load acting on the bearing, the contact point becomes an elliptical area. The small contact area provides low rolling friction, which enables ball
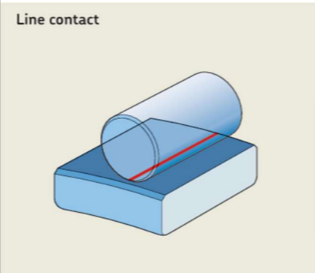
Line Contact : Rollers make line contact with the ring raceways (As shown in fig.). With increasing load acting on the bearing, the contact line becomes somewhat rectangular in shape. Because of the larger contact area and the consequently higher friction, a roller bearing can accommodate heavier loads, but lower speeds, than a samesized ball bearing.
Radial and Thrust Bearings : Rolling bearings are classified into two groups based on the direction of the load they predominantly accommodate:
Radial Bearings : Radial bearings accommodate loads that are predominantly perpendicular to the shaft. Some radial bearings can support only pure radial loads, while most can additionally accommodate some axial loads in one direction and, in some cases, both directions (As shown in fig.)
Thrust Bearings : Thrust bearings accommodate loads that act predominantly along the axis of the shaft. Depending on their design, thrust bearings may support pure axial loads in one or both directions (fig. 5), and some can additionally accommodate radial loads (combined loads, fig. 6). Thrust bearings cannot accommodate speeds as high as same-sized radial bearings.
Contact Angle : The contact angle (As shown in fig.) determines which group the bearing belongs to. Bearings with a contact angle ≤ 45° are radial bearings, the others are thrust bearings.
Bearing Terminology :
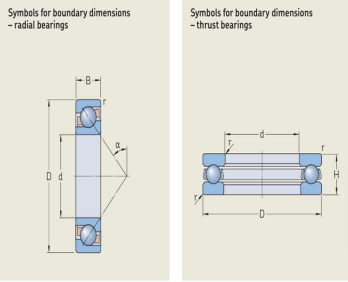
- Some frequently used bearing terms are explained here. For a detailed collection of bearing-specific terms and definitions, refer to ISO 5593 Rolling bearings – Vocabulary. Symbols used in this catalogue are mainly in accordance with ISO standards. The most common symbols are (As shown in fig.):
- d Bore diameter
- D Outside diameter
- B Bearing width
- H Bearing height
- r Chamfer dimension
- α Contact angle
Bearing Components :
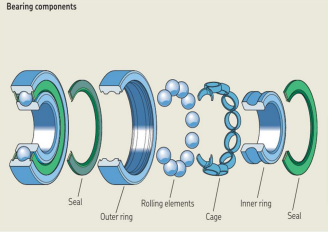
A typical rolling bearing consists of the following components (As shown in fig.) :
- an inner ring
- an outer ring
- balls or rollers, as rolling elements
- a cage
There are several bearing types capped with a seal or shield on one or both sides. Bearings capped on both sides are factory- filled with grease. They provide an economic and spacesaving solution compared to external sealing.
Conclusion : We at KEC Bearings Pvt Ltd, provides different types of bearing verities with different types of cages and design variations customised as per applications and customer requirements. For example, we are providing fibre cage in ball bearings for high RPM while we are providing C4 clearance spherical roller bearings for vibratory application. Feel free to contact for any requirement on following details
Contact Details :
KEC Bearings Pvt Ltd
G-2408A, F2 Road, Almighty Gate, Lodhika GIDC, Metoda – 360021, Rajkot, Gujarat (INDIA)
Email: sales@kecbearings.com
WhatsApp: +91 9330 96 9330
Website: www.kecbearings.com

